153-0373-2222
138-3908-0089
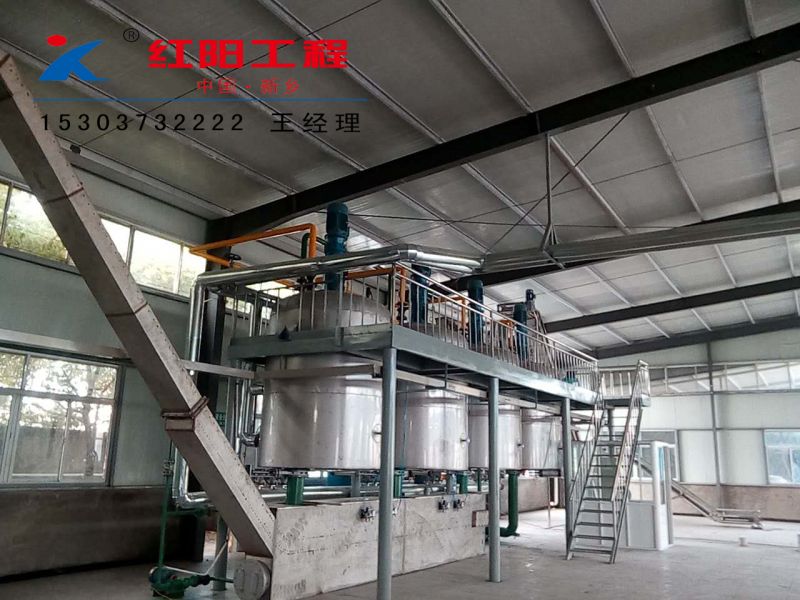
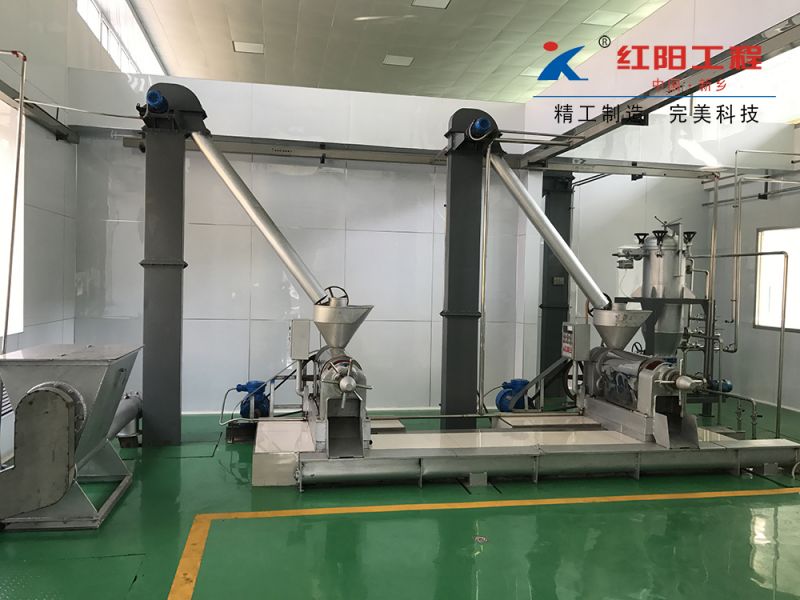
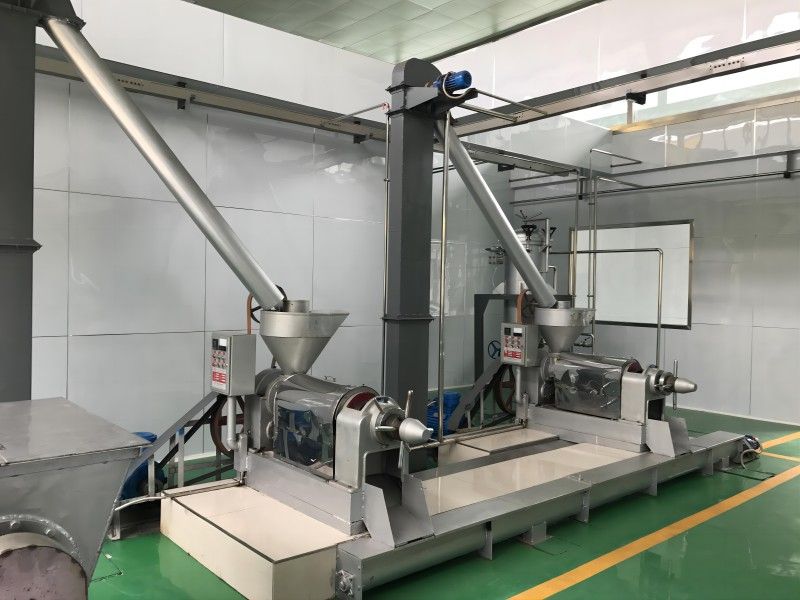
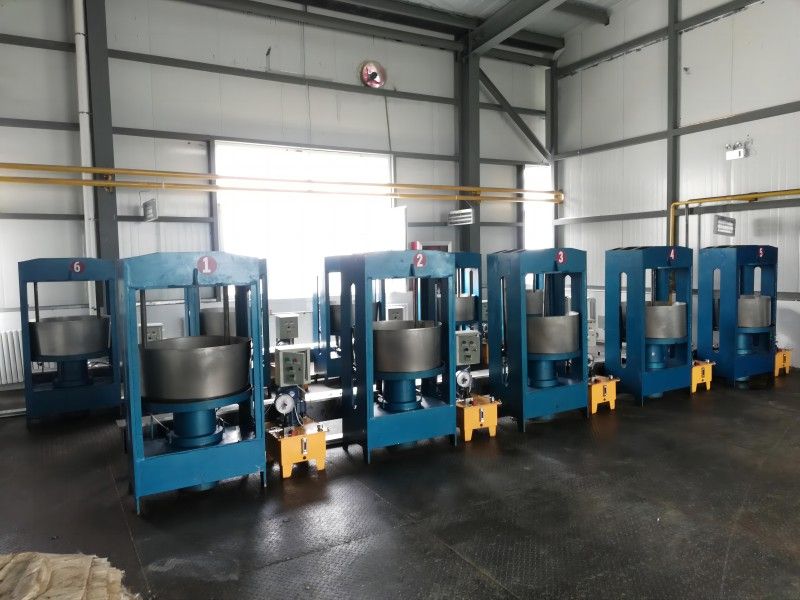
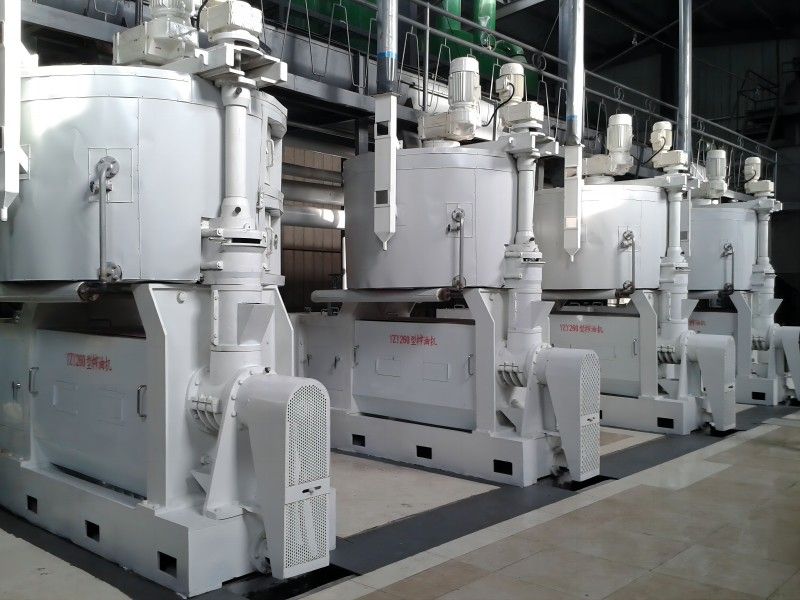
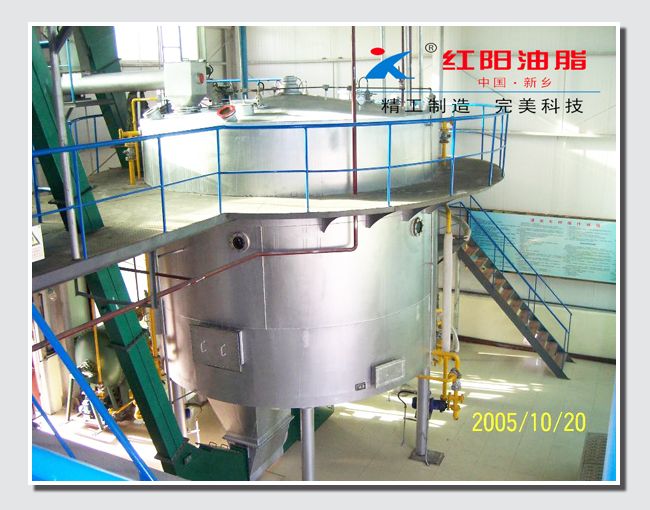
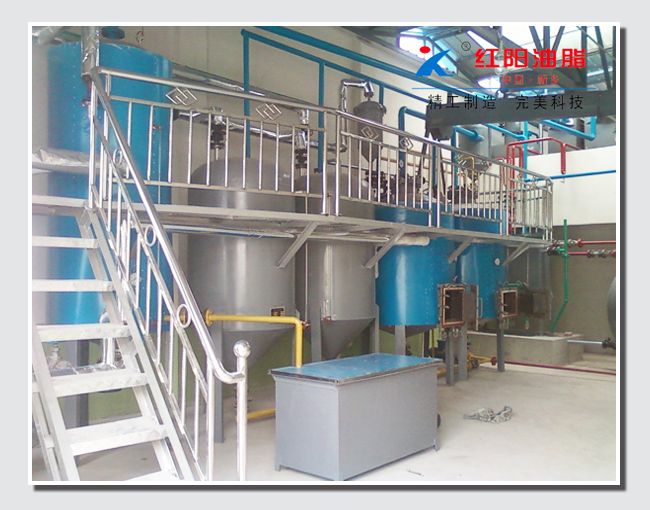
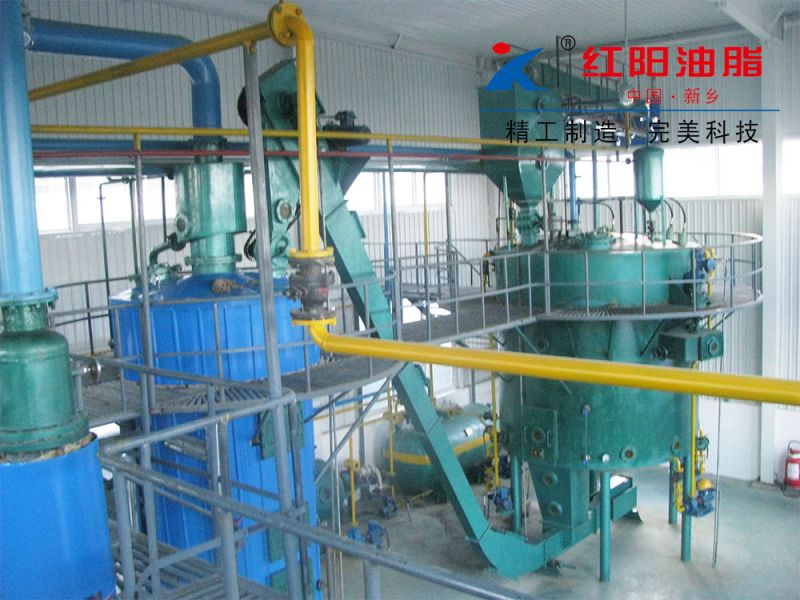
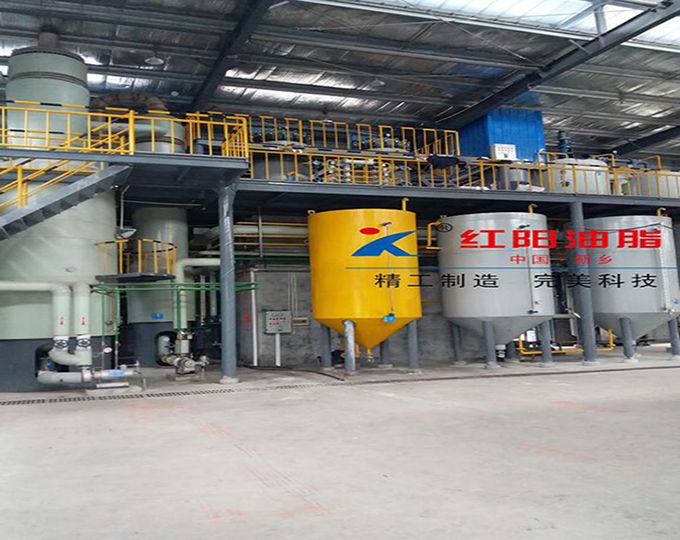
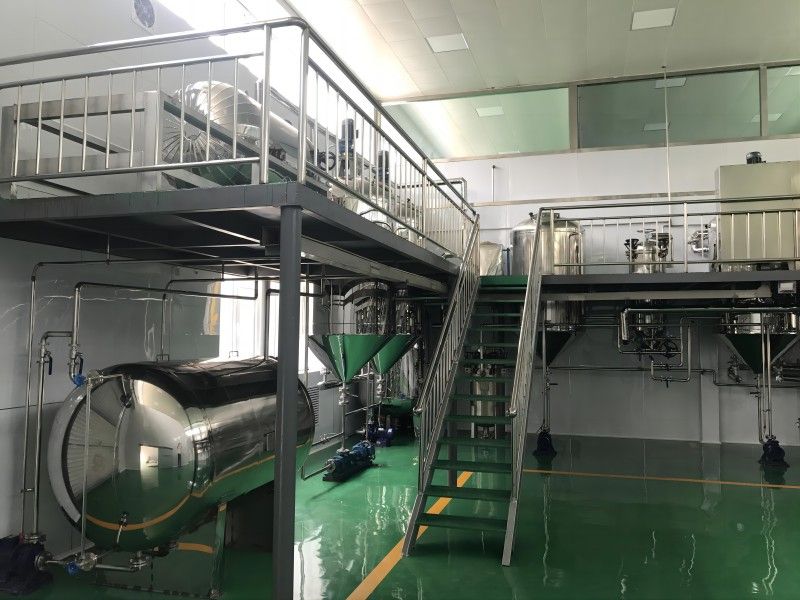
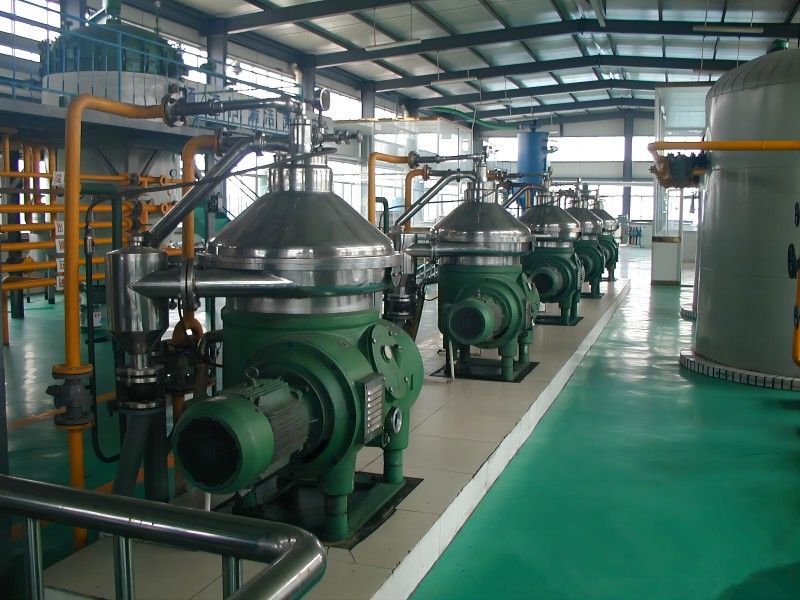
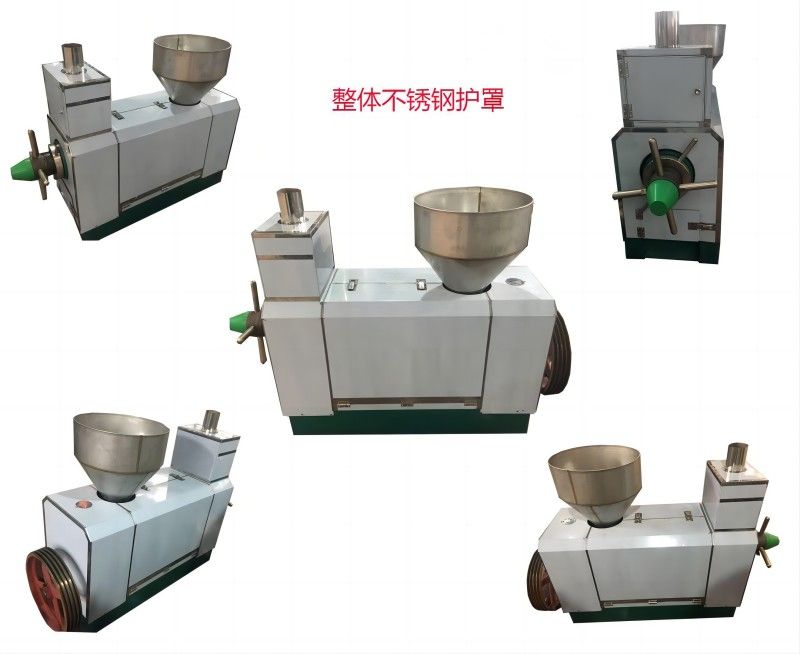
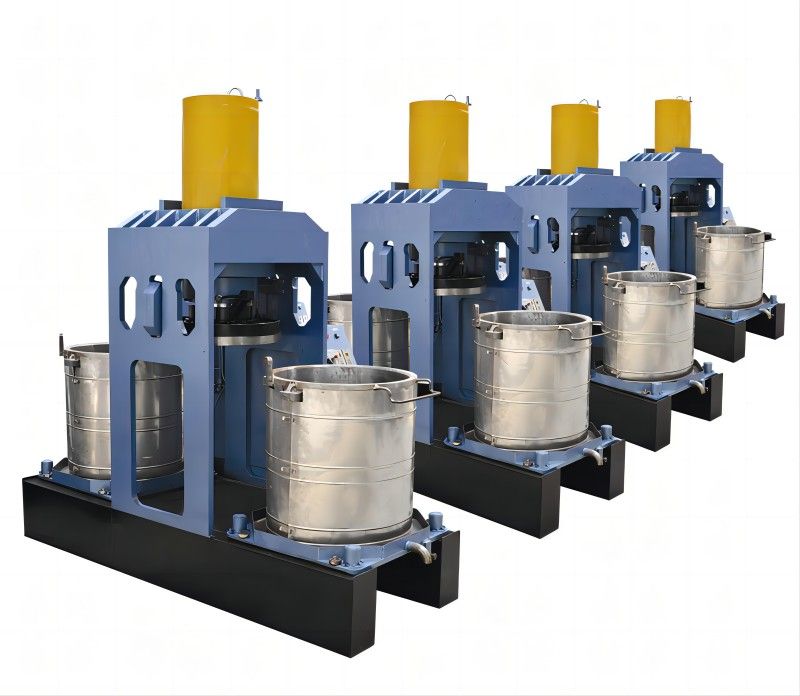
Walnut Oil Refining Equipment - Physical Refining Equipment
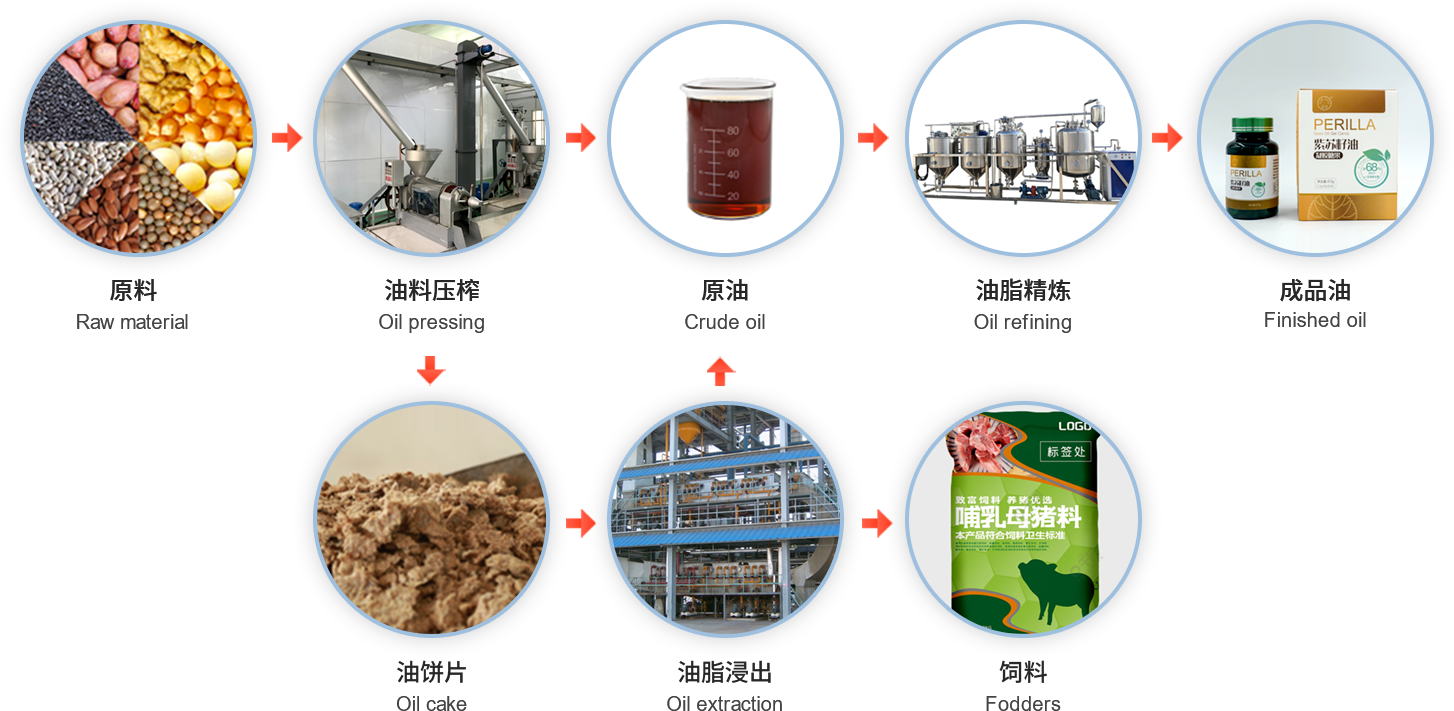
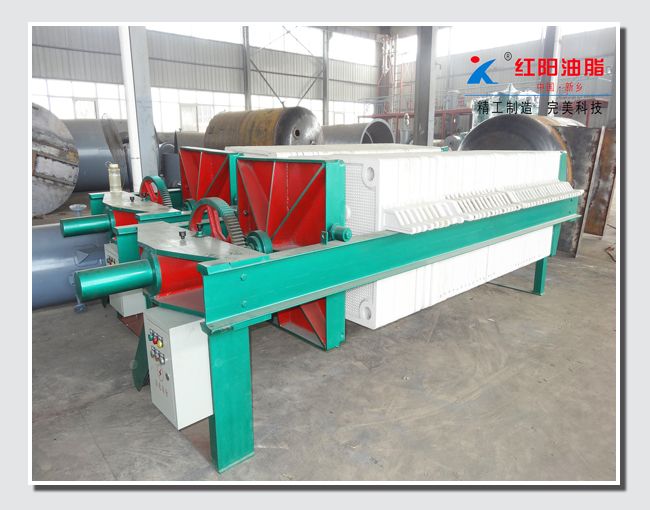
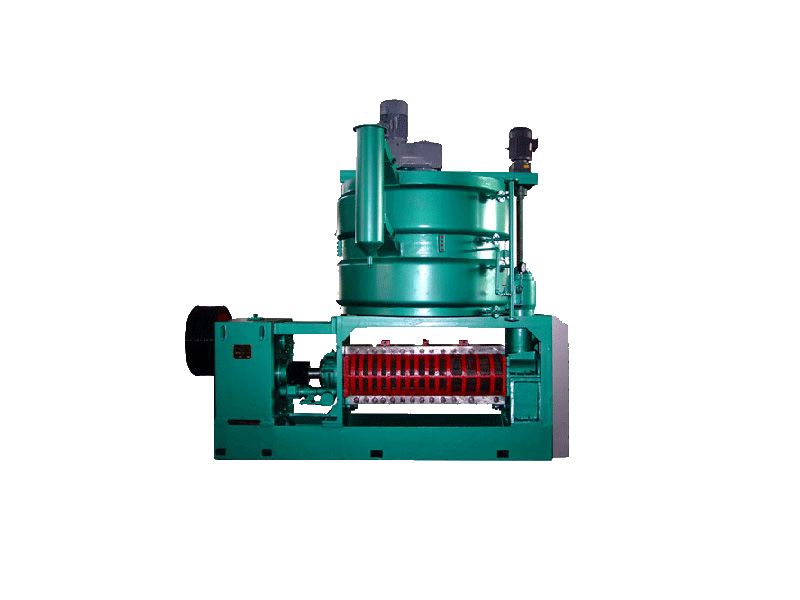
Physical refining is a process in which crude oil undergoes de-gumming, de-acidification, de-coloring, and de-odorization to remove non-glyceride components.
Among these, de-acidification is one of the key processes in oil refining, aimed at removing free fatty acids from the crude oil while also removing some impurities such as pigments, phospholipids, hydrocarbons, and mucilage, as well as beneficial components like tocopherols, sterols, and sterol esters. The methods currently used in industrial production for de-acidification mainly include traditional methods such as chemical de-acidification, physical de-acidification (or steam refining), and mixed oil de-acidification. Many oil scientists have developed new de-acidification methods, including biological de-acidification (or biorefinery), chemical re-esterification de-acidification, solvent extraction de-acidification, supercritical extraction de-acidification, membrane separation technology de-acidification, molecular distillation de-acidification, and liquid crystal de-acidification. Although these new methods overcome the shortcomings of traditional de-acidification methods, they also have their limitations.
Traditional de-acidification methods typically refer to those used in industrial production, including chemical de-acidification, physical refining (or de-acidification), and mixed oil refining (or de-acidification).
Chemical de-acidification, also known as alkali refining, is widely used in industry. Typically, alkali solution is added to the degummed oil, causing the alkali to react with free fatty acids, precipitating them as soap stock. Some impurities are also adsorbed by the soap stock, which is then separated by centrifugation. Chemical de-acidification usually uses caustic soda (sodium hydroxide). Neutral oils undergo hydrolysis under the action of alkali, resulting in significant oil loss; in addition, neutral oils entrained in the soap stock also lead to neutral oil loss. The soap stock needs to be treated with sulfuric acid, leading to a large amount of wastewater and environmental pollution. The amount of oil loss depends on the acid value of the crude oil; the higher the acid value, the greater the oil loss. This method is relatively thorough in de-acidification and stabilizes the oil quality.
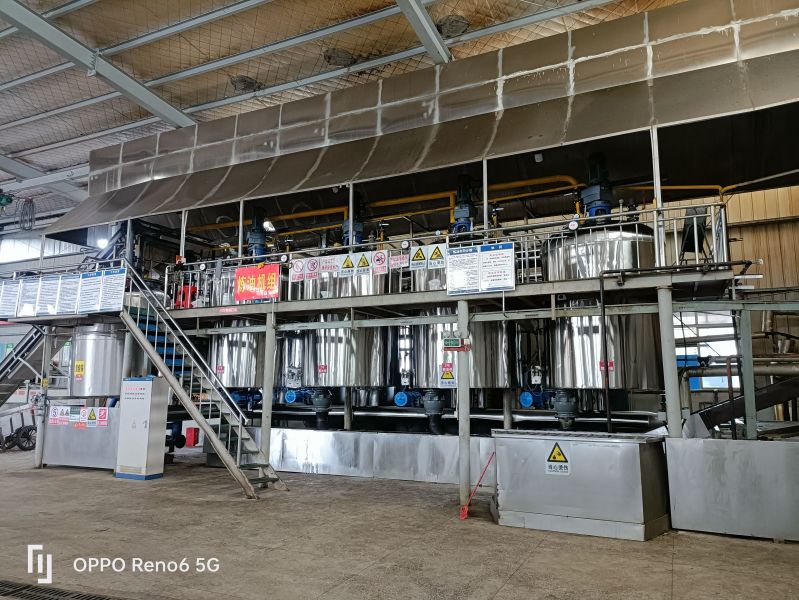
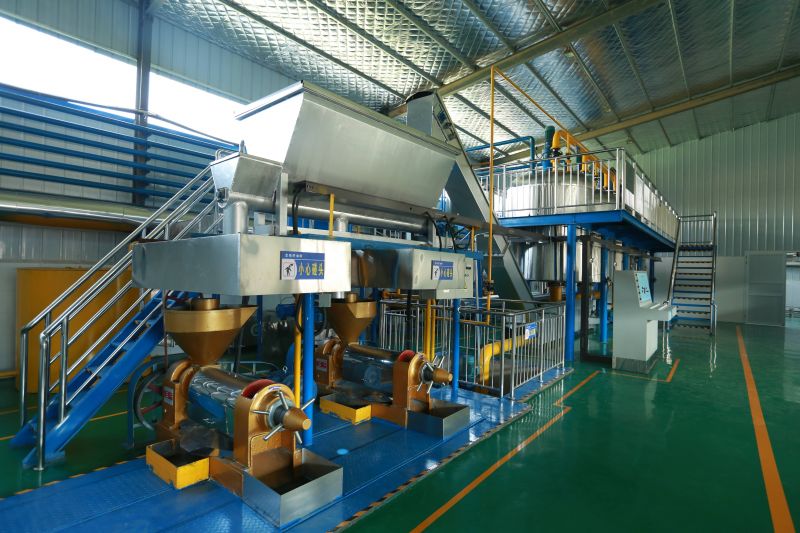
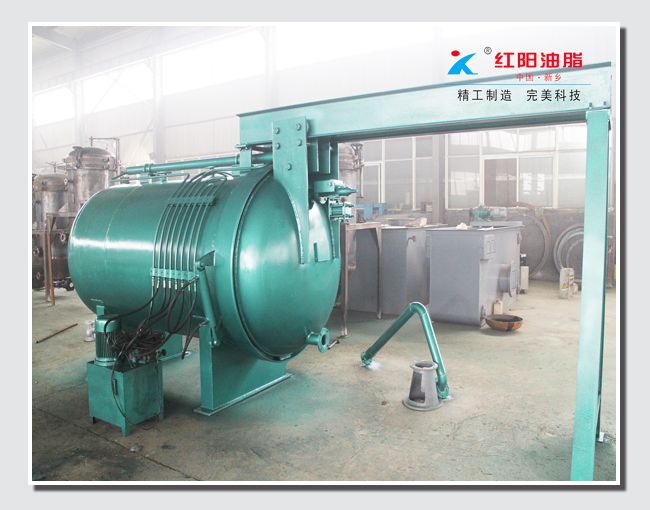
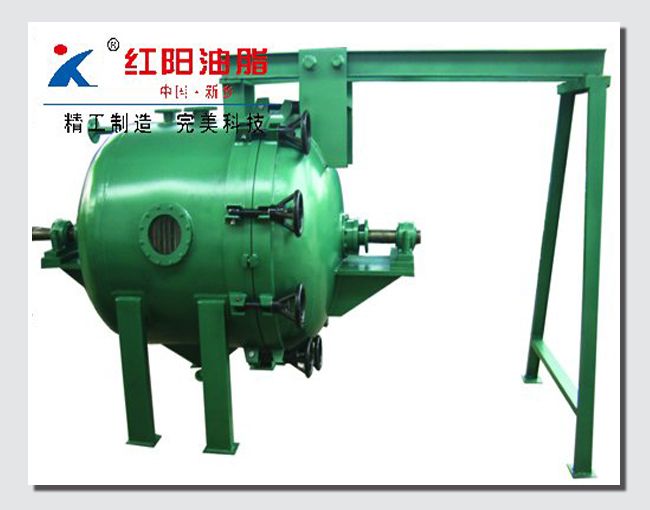
Physical de-acidification, also known as steam refining, is performed under high vacuum conditions. Steam is introduced into the oil to carry away acid value, non-saponifiable matter, and odor-causing substances. Compared with chemical de-acidification, this method does not produce soap stock, resulting in lower oil loss and higher oil quality. It also has the advantages of simple operation, requiring less steam, water, and power, and lower investment. Some heat-sensitive pigments (carotenoids) and odor-causing substances are also removed with the steam stripping. Compared with alkali refining, physical de-acidification has the advantages of high production capacity, no soap stock production, reduced overflow, and reduced environmental pollution. However, it also has the disadvantages of strict pre-treatment requirements for crude oil, unsuitability for heat-sensitive cottonseed oil, and the formation of polymers and trans fatty acids under high temperatures.
In recent years, the development of the oil industry in China has been rapid, with many advanced foreign oil physical refining equipment and production lines being introduced into the country. At the same time, many old oil mills have been expanding and upgrading. Therefore, it is urgent to upgrade the refining production lines of a large number of oil companies in China to adapt to the new market situation.
According to the national conditions, the specific conditions of small and medium-sized enterprises, and the trend of promoting physical refining in oil production, Xinxiang Hongyang Machinery Co. Ltd. has developed a new process suitable for the transformation and upgrading of small and medium-sized oil enterprises in China. The main problems in the domestic oil refining industry are mainly manifested in the instability of product quality, poor economic and technical indicators, inadequate de-coloring and de-odorization, the widespread presence of "four color" challenges, unreasonable treatment of by-products, high consumption, low yield, and especially the poor solution of "three wastes" pollution, which cannot meet the requirements of clean production and environmental protection. These problems are particularly severe in small and medium-sized oil enterprises in China and require an industry-wide transformation and upgrading. Although the advanced refining lines imported from abroad have advanced technology, they are too costly to be quickly and widely adopted by small and medium-sized oil enterprises in China. In response to the challenges and shortcomings in the physical refining technology of medium-sized oil processing enterprises in China, Hongyang Company has developed a new physical refining technology suitable for the main edible vegetable oils produced in China (rape seed oil, soybean oil, sunflower seed oil, cottonseed oil, and rice bran oil, etc.), aiming to produce high-grade oil products and solving the serious pollution problems in oil refining. The technical and economic indicators of this new technology have reached the advanced level both domestically and internationally, and the complete set of physical refining equipment production line has been designed, manufactured, installed, and put into production, with the technology being certified and operational.