153-0373-2222
138-3908-0089
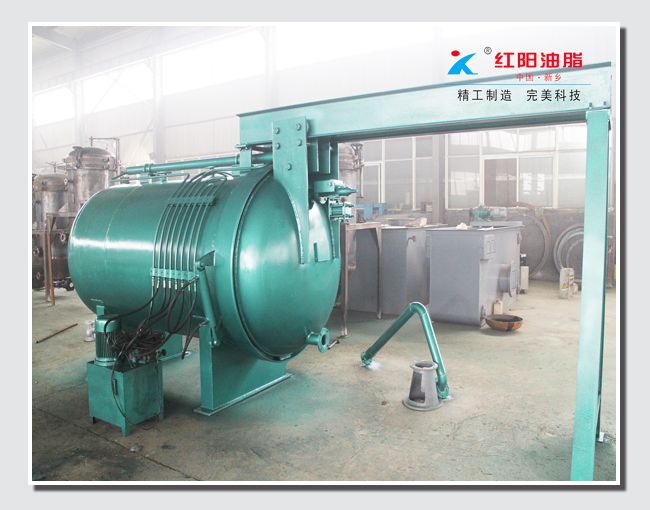
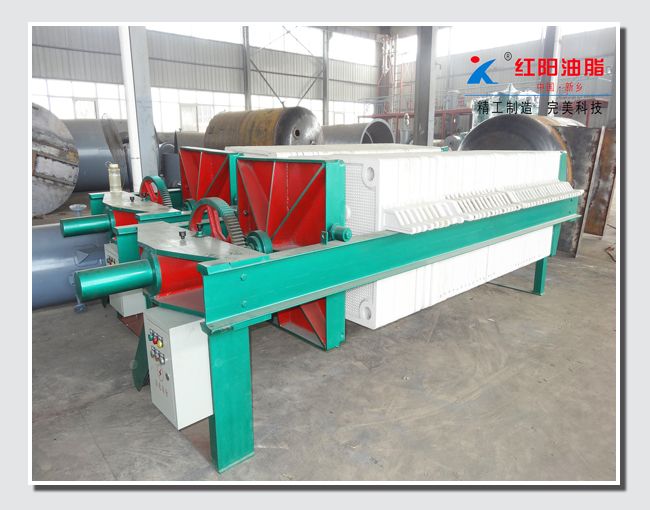
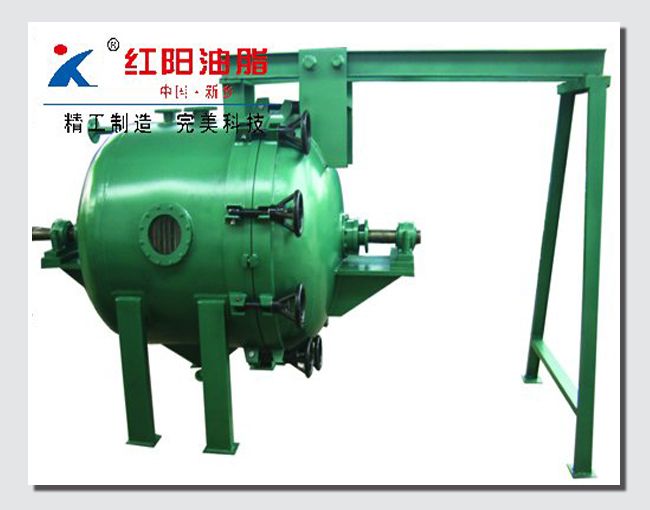
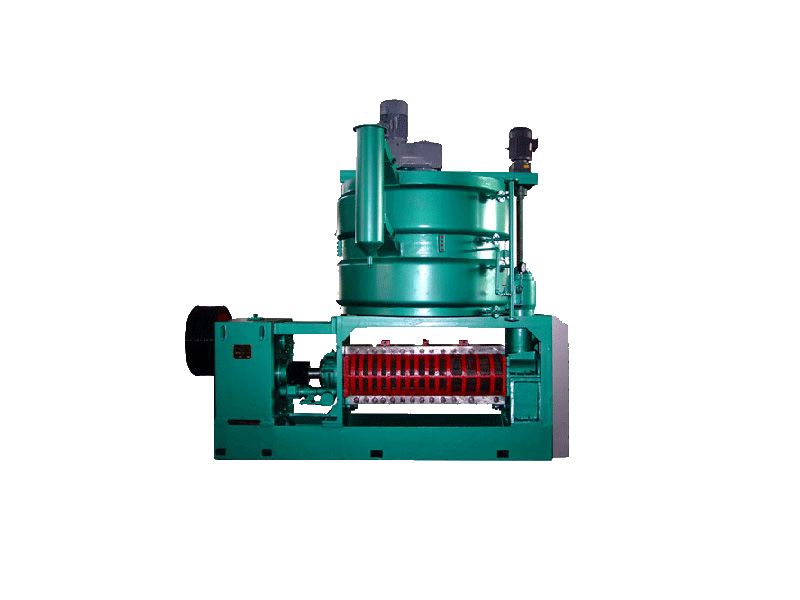
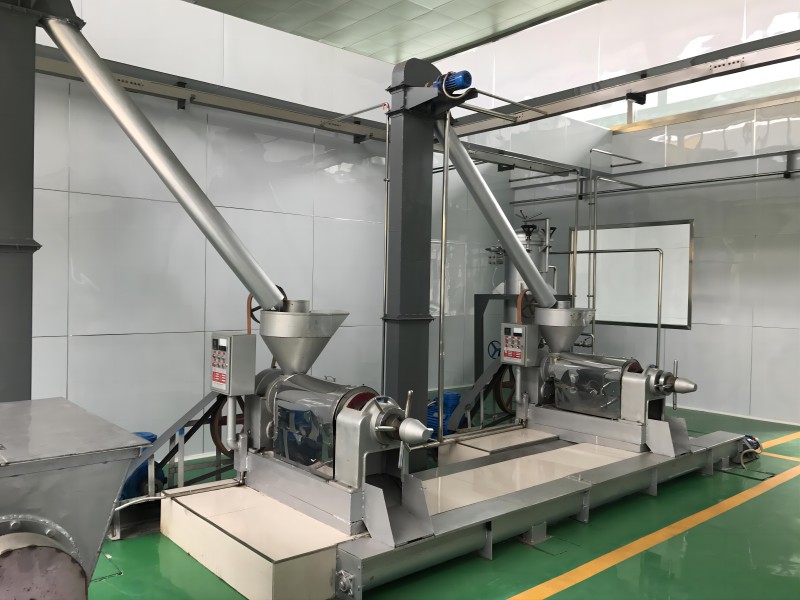
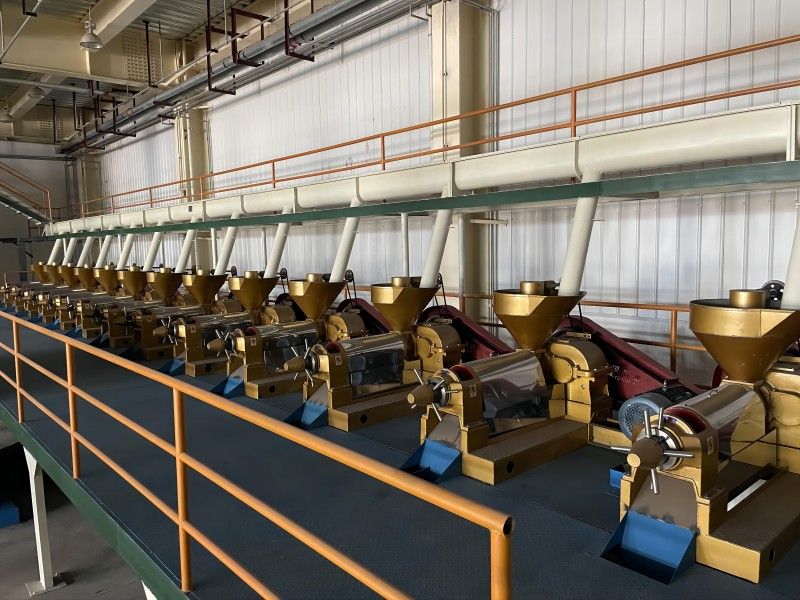
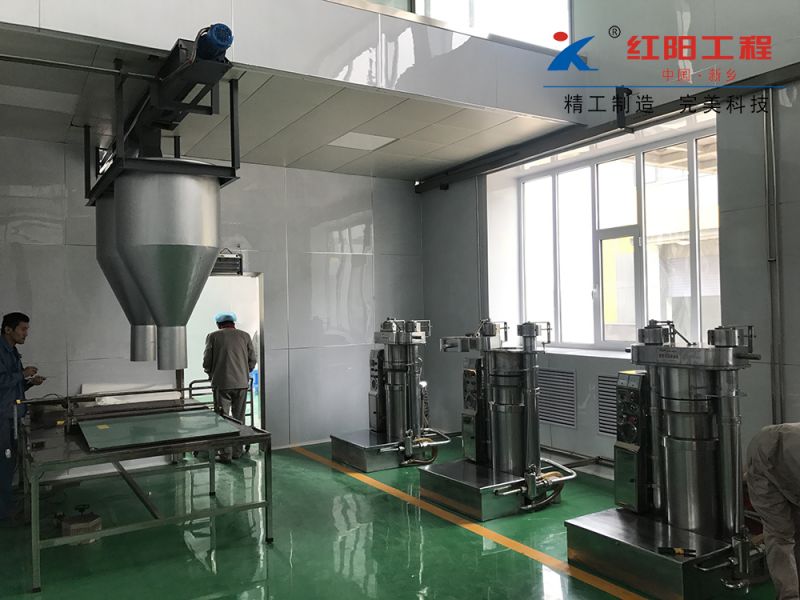
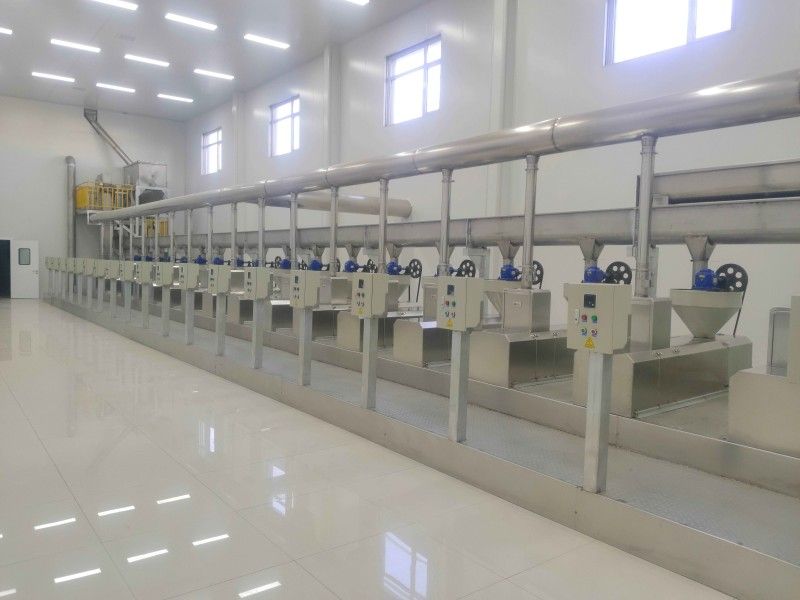
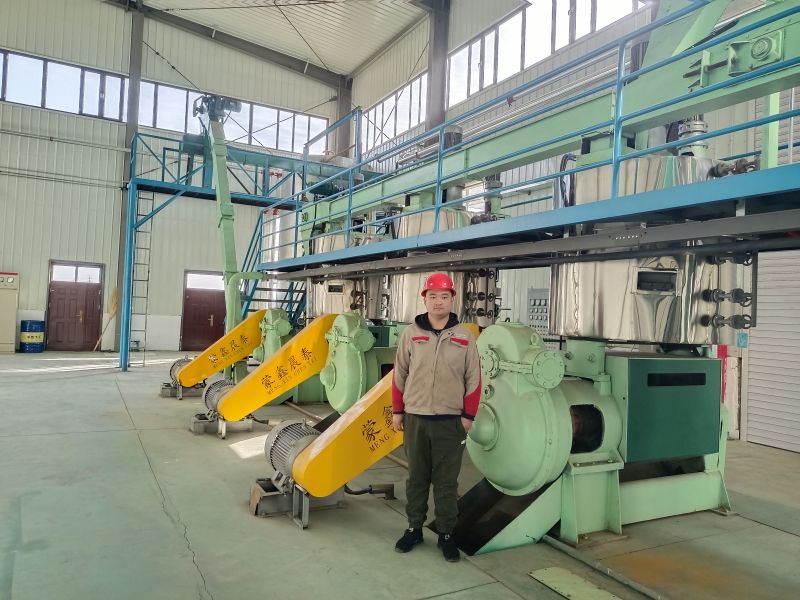
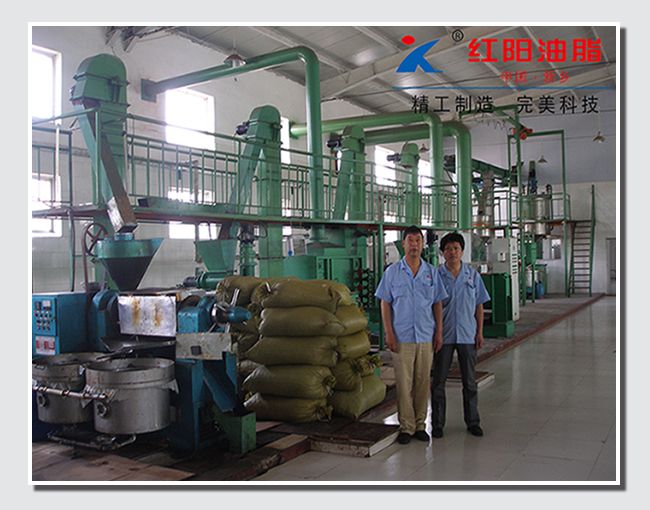
Grape Seed Oil Equipment
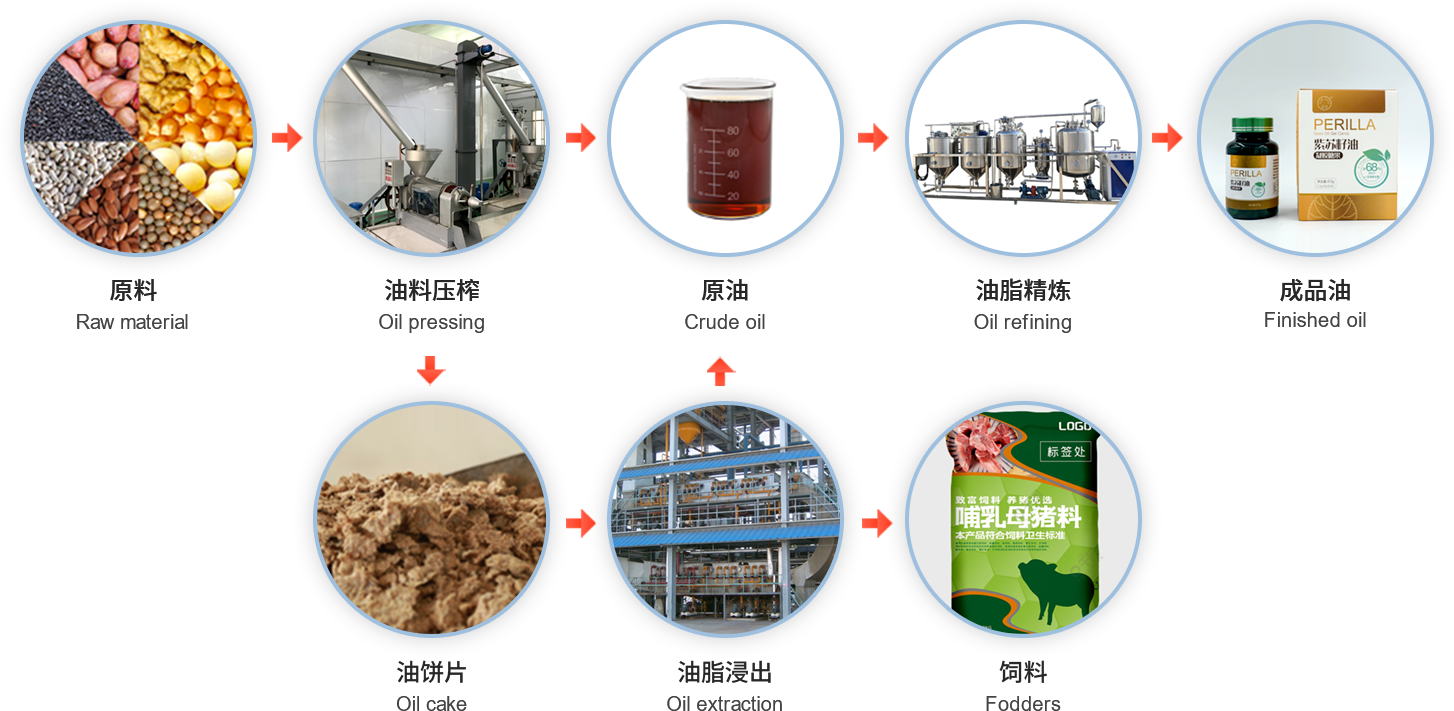
oilseeds refer to plant materials used for oil extraction, generally including plants with an oil content of over 10% that are valuable for oil extraction. Examples include seeds of grapes, soybeans, cotton, sesame, and rapeseed; nuts of peanuts and coconuts; fruits of oil palm and olive; underground tubers of oil yam; embryos of corn and wheat; and rice bran, and others. Grape seed oilseeds can be categorized into edible and medicinal oilseeds based on their economic use. Any raw material that can be used to extract edible oil, such as grape seeds, soybeans, peanuts, cottonseeds, sesame, rapeseeds, tea seeds, corn embryos, and rice bran, is considered an edible oilseed. According to botanical classification, vegetable oilseeds can be divided into herbaceous and woody types. Oilseeds produced by trees or shrubs are called woody oilseeds, such as grape seeds, tea seeds, oil tung, and olive oil, while those produced by herbaceous plants are called herbaceous oilseeds, such as sesame, peanuts, and rapeseeds. Herbaceous oilseeds are the main source of oilseeds, primarily consisting of seeds.
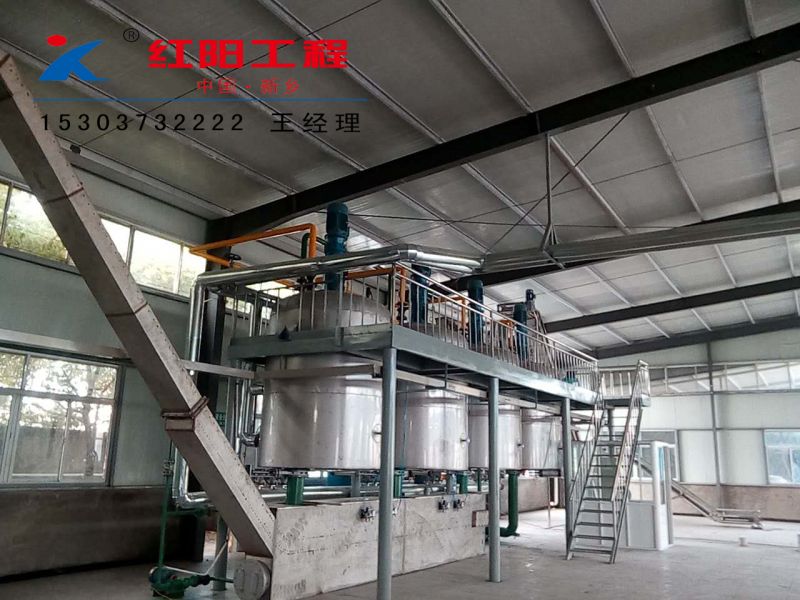
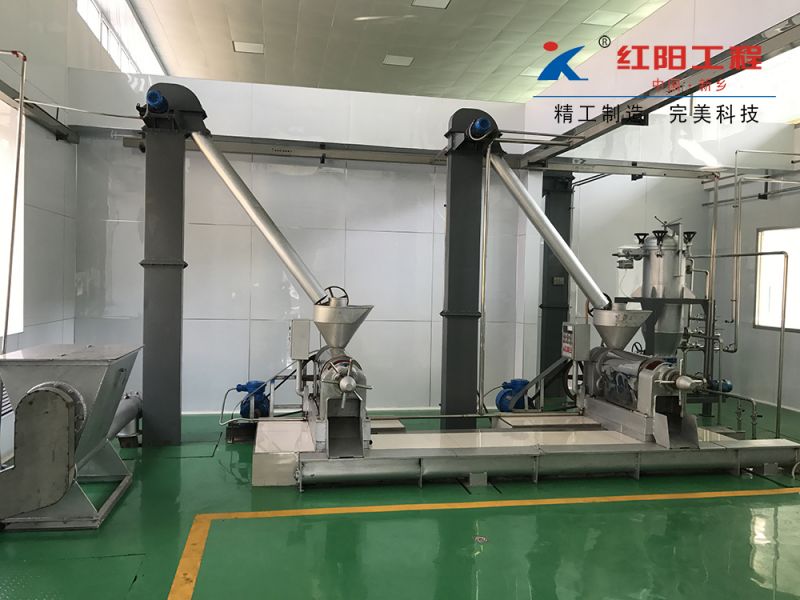
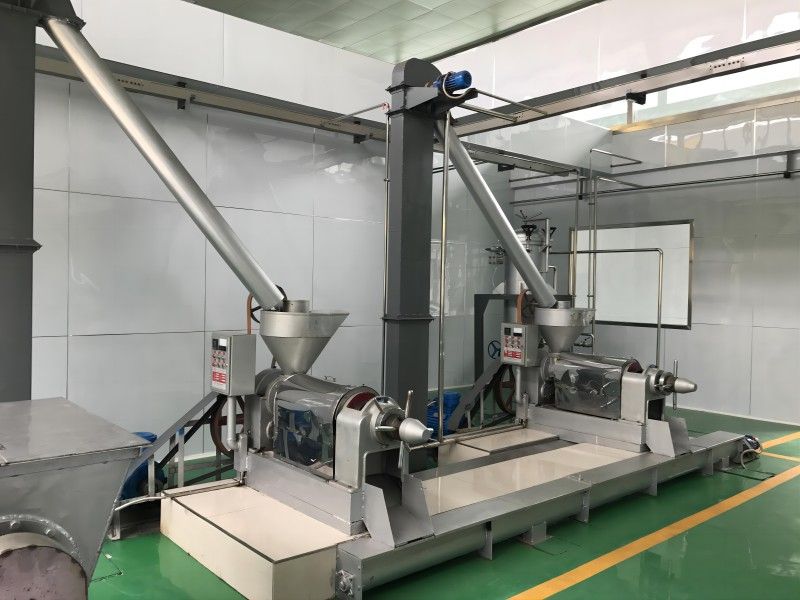
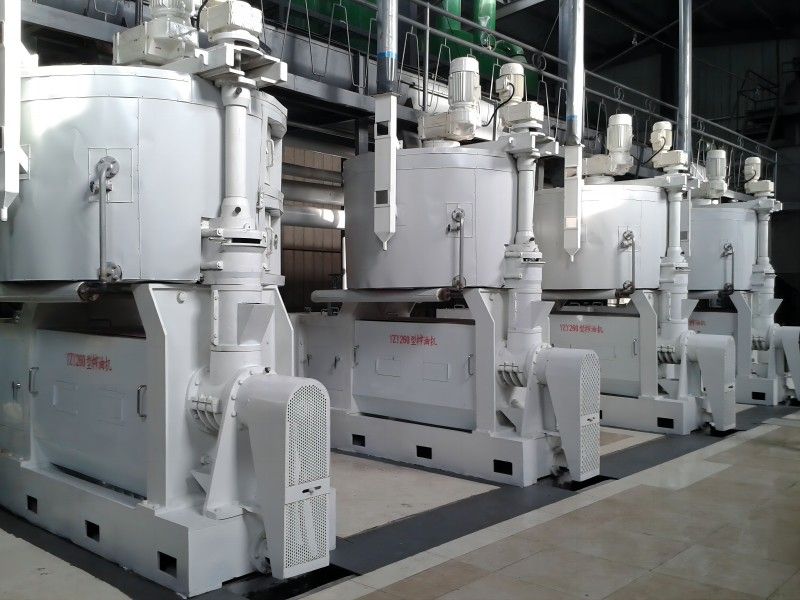
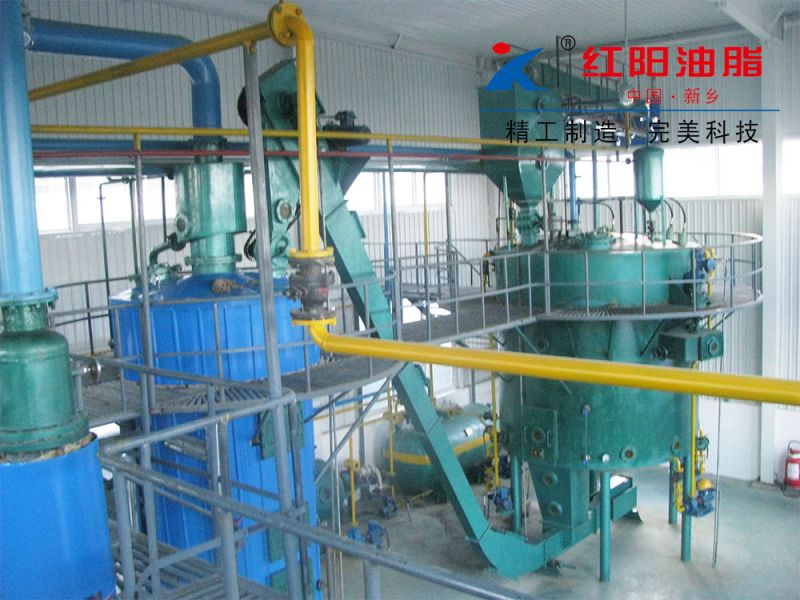
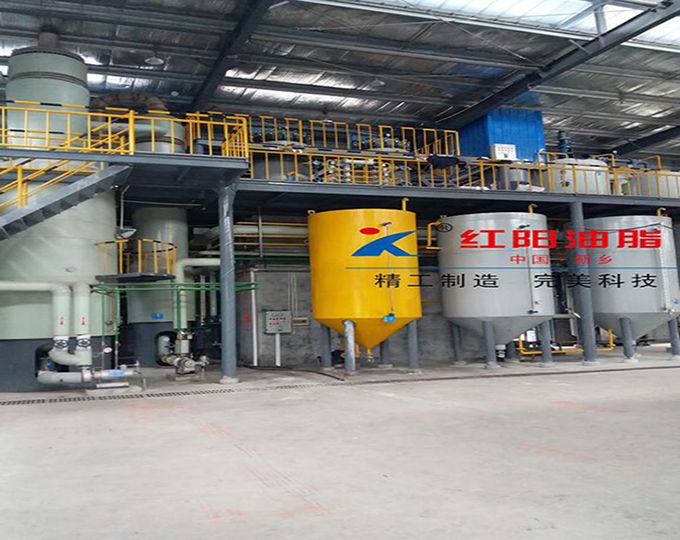
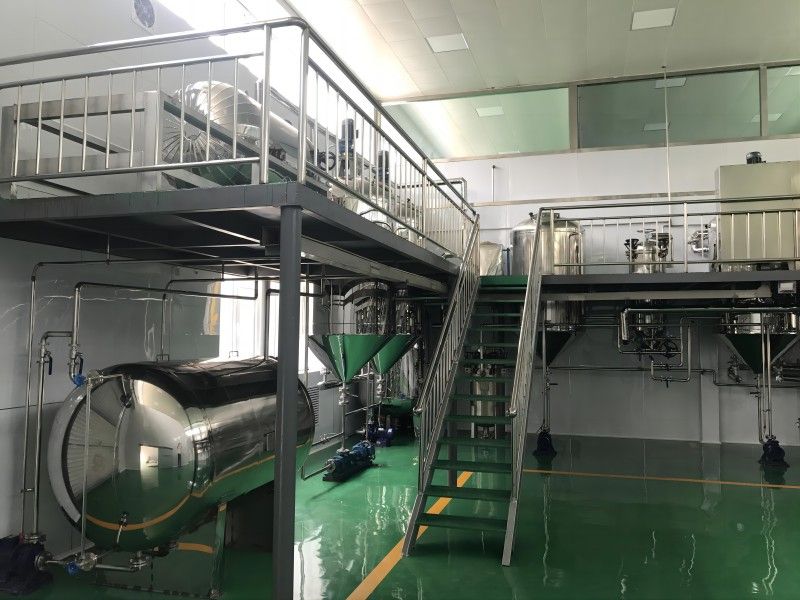
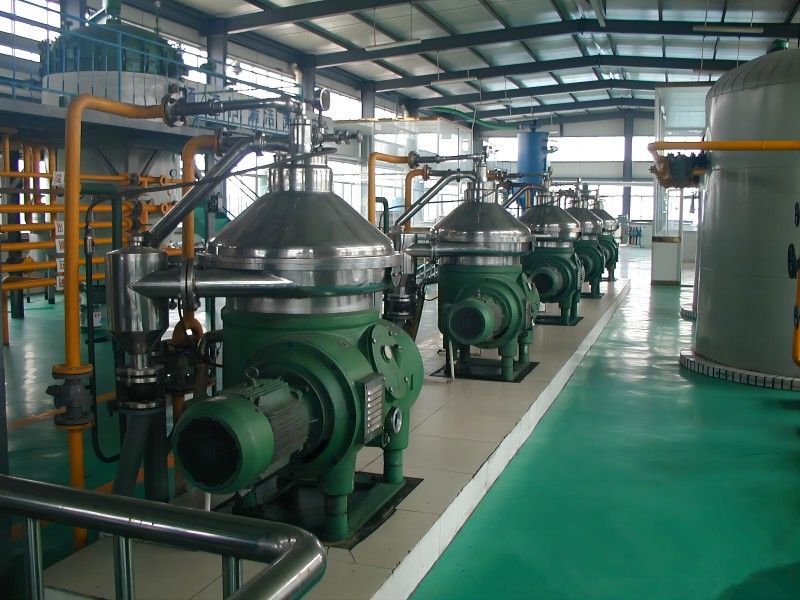
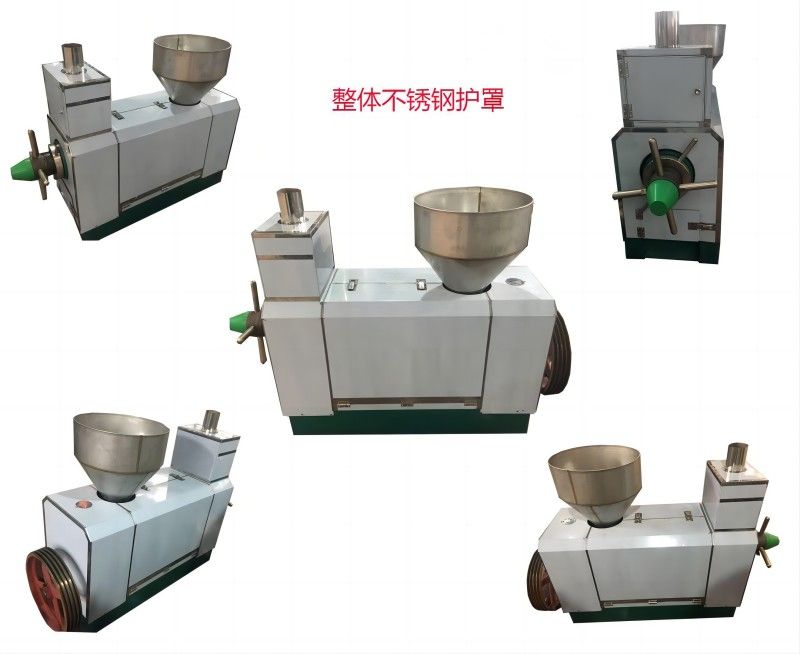
Characteristics of Grape Seed Pressing Method for Oil Extraction
(1) Strong adaptability
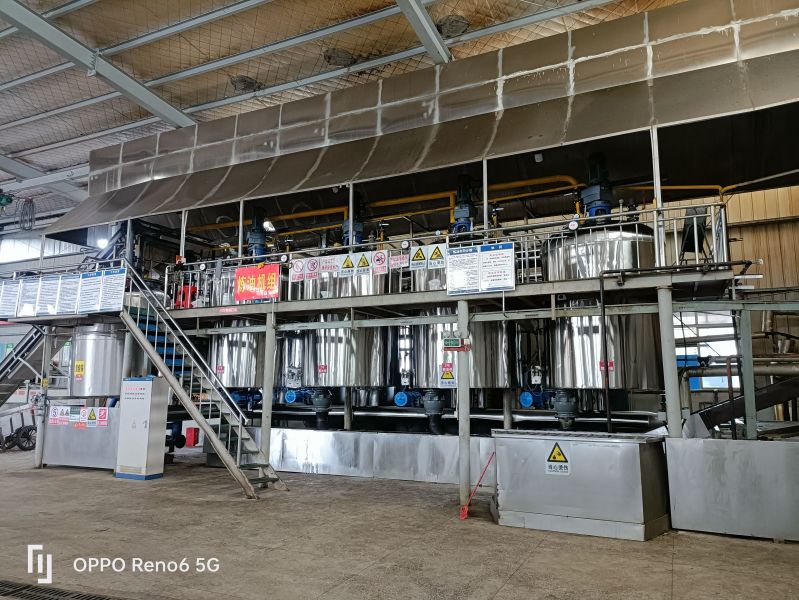
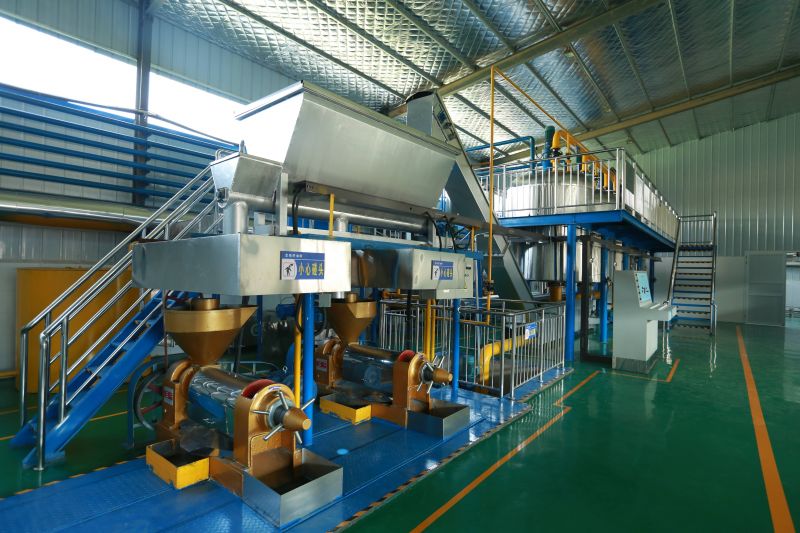
The pressing method is suitable for processing various oilseeds and can be applied to production on different scales. It does not require high power equipment and can utilize electricity or other power sources, offering flexibility and convenience, especially in areas with underdeveloped industry or poor transportation.
(2) Simple and easy-to-operate process
Usually, the oilseeds can be pressed after pretreatment, with a short technological process and low technical requirements for operation. The supporting equipment can be a combination of traditional and modern, with low investment and quick results. When using small oil presses, direct fire can be used to roast the seeds, and whole seeds can be pressed, although the quality of the crude oil obtained may be poorer.
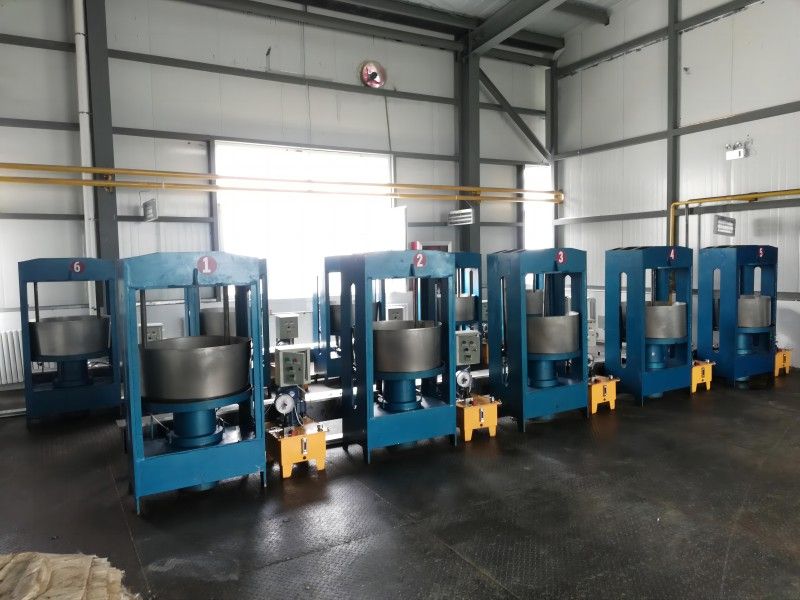
(3) Relatively safe production
During the production process, the oil press machinery operates smoothly with a slow rotation speed of the main shaft, such as 8 rpm for ZX·18, 15 rpm for ZY·24, and 28-35 rpm for ZX·10. Generally, no accidents will occur as long as the production operation procedures are followed.
(4) Disadvantages
The main disadvantages of the pressing method include a higher residual oil rate in the press cake compared to the leached meal, a significant labor intensity during repair and replacement of wearable parts, and poorer product quality in small-scale plants with rudimentary production conditions.
Due to these limitations, especially the higher residual oil rate in the press cake, which can generally reach 5%-8%, it is necessary to integrate the pressing method with the extraction method to further extract the residual oil from the press cake and reduce production costs.